Known as rare diseases, autoimmune diseases affect about 20% of the world population. Symptoms vary from one disease to another, but some symptoms can put you “on guard” to get to the doctor. We tell you what they are.
What are they?
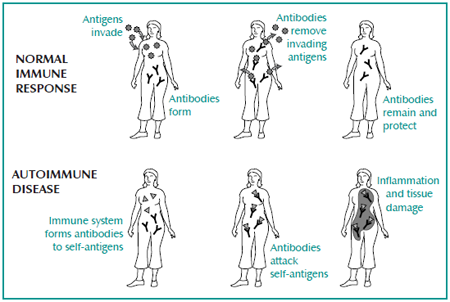
The immune system is the body’s protective barrier. It consists of a set of organs, tissues and cells that release proteins, called antibodies, and a certain type of white blood cells (lymphocytes). Lymphocytes have the role of protect us from bacteria, viruses or parasites that can lead to the onset of infection. In case of autoimmune diseases, the immune system receives false signals and act not only against any external threats, but also attack healthy tissues and organs in the body, which may result in stop functioning.
Which is the cause?
In some cases, the immune system “lay oneself out” without having a reason, but in other cases foreign substances that enter the body have a similar composition to another substance that is usually found in your body. The immune system can not distinguish them and therefore attacking healthy cells. And when some substances in the body changes its structure, the immune system may perceive as a threat and therefore will produce antibodies against them. Also, repeated infections, stress, excessive vaccination and certain medications can lead to the onset of autoimmune diseases.
How is it diagnosed?
So far, we have identified about 80 of which are for autoimmune diseases, which makes diagnosis more difficult, because their signs are varied. In addition, the symptoms do not occur every day, but on the contrary, it may take longer time to cause health problems. Detection tests are needed in case of disease, while for others it requires a long monitoring of symptoms to correct diagnosis. Most autoimmune diseases affecting the skeletal system and the digestive system, and among the most common symptoms include chronic fatigue, fever, joint and muscle pain, malaise and skin rashes.
[adsense][adsense]